Acoustic Neuroma Treatment
Effective solutions for acoustic neuroma. Contact us for a consultation today.

Overview
Acoustic neuroma, also known as vestibular schwannoma, is a non-cancerous tumour that develops on the main nerve leading from your inner ear to your brain. While benign, it can cause significant symptoms and complications if left untreated. Addressing acoustic neuroma promptly is crucial to prevent hearing loss and other neurological issues. At The Forbury Clinic, we offer specialised care and advanced treatment options to manage and treat acoustic neuroma effectively.
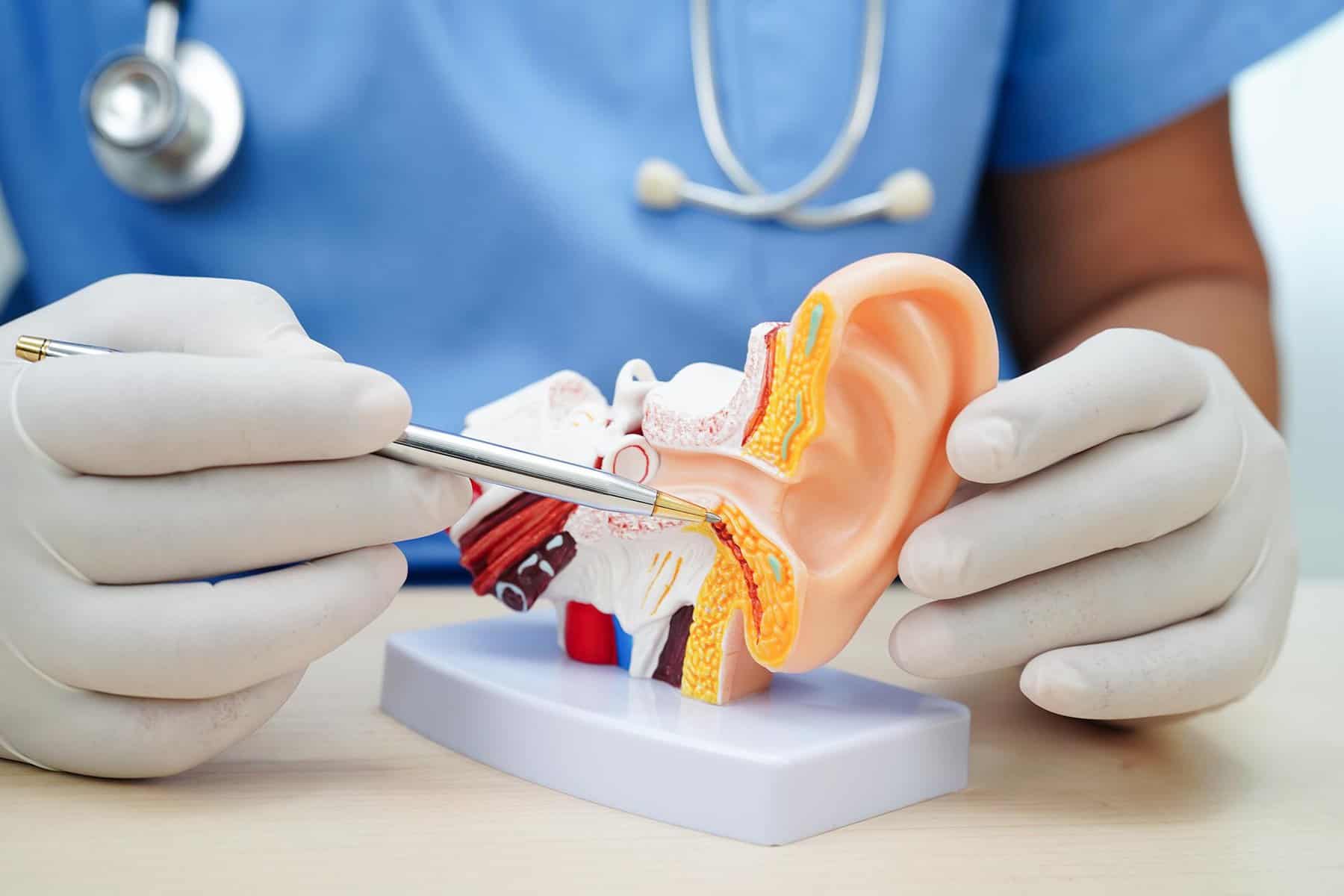

What is Acoustic Neuroma?
Acoustic neuroma is a slow-growing tumour that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain. This nerve is responsible for hearing and balance, and a tumour in this area can cause a variety of symptoms.
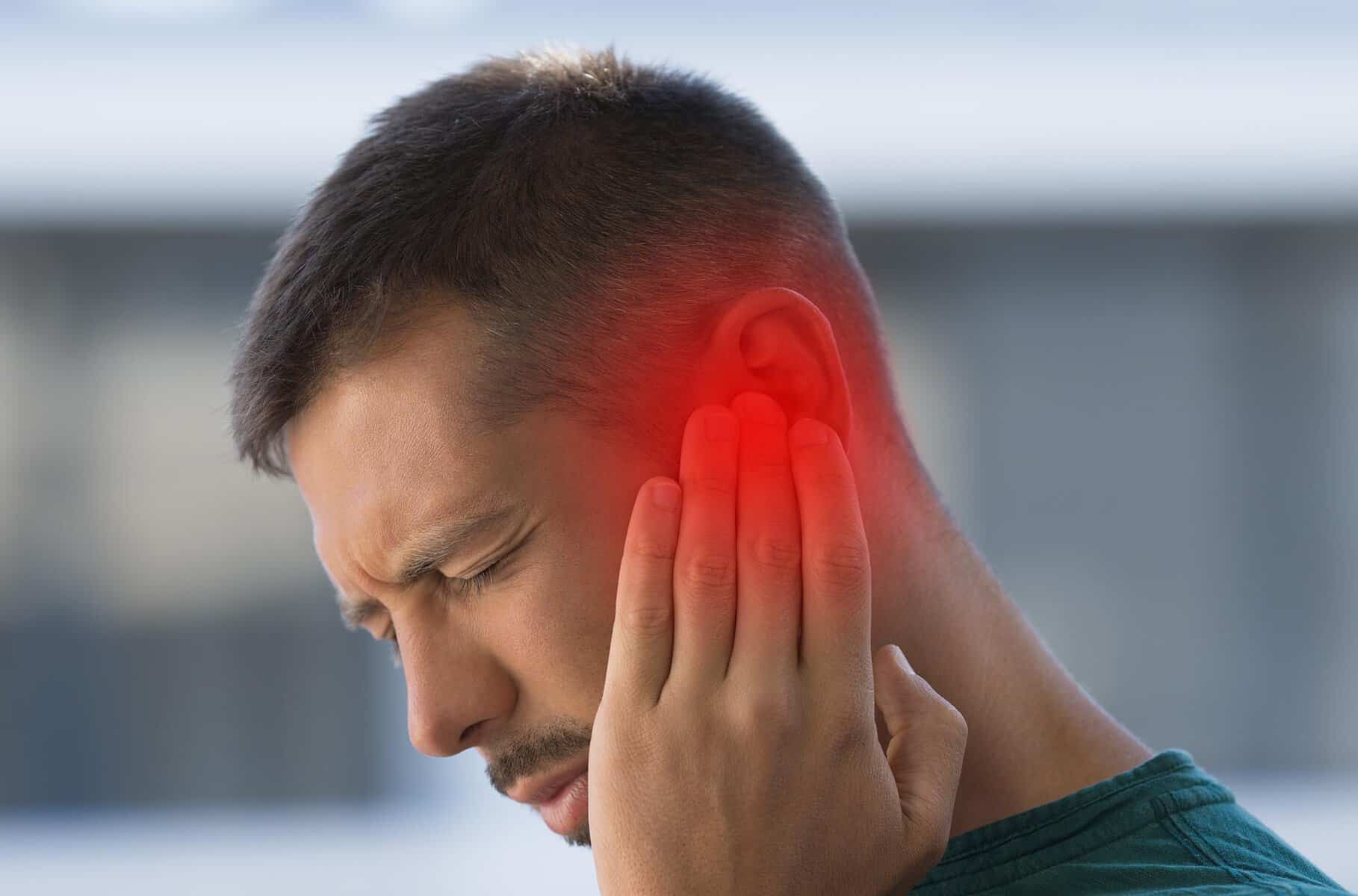
Common symptoms and signs include:
- Hearing loss, usually gradual and in one ear
- Ringing (tinnitus) in the affected ear
- Unsteadiness or loss of balance
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Facial numbness or weakness (less common)
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes
The exact cause of acoustic neuroma is unknown, but several factors may contribute to its development:
Genetic Factors:
A small percentage of cases are linked to neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a genetic disorder.
Radiation Exposure:
Previous exposure to radiation, particularly to the head and neck, may increase the risk.
Age:
Most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 60.
Risk Factors
Risk factors contributing to the development of acoustic neuroma include:
Family history of neurofibromatosis type 2
Exposure to loud noise
History of radiation treatment to the head
Diagnosis
Diagnosing acoustic neuroma involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Medical History Review: Assessment of symptoms and previous health issues.
- Hearing Tests: Audiometry to evaluate hearing loss and its pattern.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to visualise the tumour and determine its size and location.
- Balance Tests: Electronystagmography (ENG) or videonystagmography (VNG) to assess balance function.

Treatment Options
Effective treatment for acoustic neuroma depends on the size of the tumour, its growth rate, and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
Monitoring:
Regular MRI scans to track the tumour’s growth, particularly for small, slow-growing tumours.
Radiation Therapy:
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Precise radiation to shrink the tumour while minimising damage to surrounding tissue.
- Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy (FSRT): Radiation delivered in several small doses over time.
Surgery:
- Microsurgical Removal: Complete or partial removal of the tumour through a procedure such as translabyrinthine, retrosigmoid, or middle fossa approach.
At The Forbury Clinic, we offer innovative treatments and personalised care plans to manage acoustic neuroma effectively.
Managing Acoustic Neuroma
Managing acoustic neuroma involves:
Regular Monitoring:
Ongoing MRI scans to detect any changes in the tumour’s size.
Symptom Management:
Medications or therapies to address symptoms such as dizziness and hearing loss.
Hearing Aids:
Devices to improve hearing function if hearing loss is significant.
Complications and Prognosis
If left untreated, acoustic neuroma can lead to serious complications, including:
- Persistent and worsening hearing loss
- Balance problems and increased risk of falls
- Pressure on the brain stem, which can be life-threatening
- Facial nerve damage, causing numbness or paralysis
With timely and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for acoustic neuroma is generally good, though regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence.
Why Choose The Forbury Clinic?
The Forbury Clinic offers expert care and advanced treatments for acoustic neuroma. Our dedicated team of specialists uses cutting-edge technology to provide accurate diagnoses and personalised treatment plans. We prioritise patient-centred care, ensuring each patient receives the attention and support they need. Choose The Forbury Clinic for expert care, state-of-the-art facilities, and a compassionate approach to managing acoustic neuroma.
