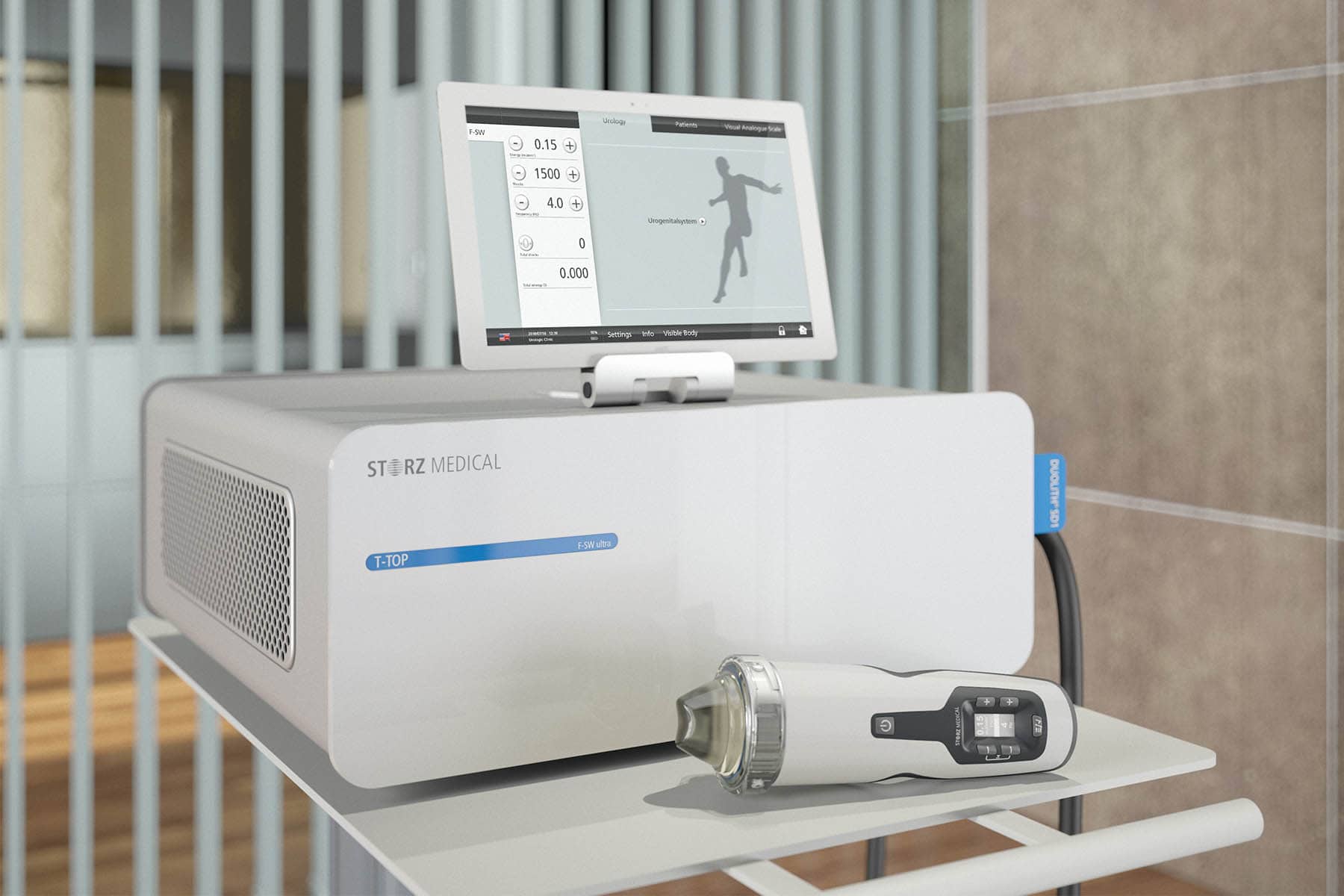
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that has gained popularity for its ability to stimulate healing and improve blood flow. Originally developed to treat kidney stones, this innovative therapy is now widely used in orthopaedics, sports medicine and erectile dysfunction treatment. With minimal downtime and proven effectiveness, shockwave therapy is a well-regarded solution for individuals looking for non-surgical treatment.
What is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a medical treatment that uses acoustic waves to promote healing and regeneration in damaged tissues. There are two main types of shockwave therapy:
- Focused shockwave therapy is a non-invasive medical treatment that uses high-energy sound waves to target specific areas of the body for healing and pain relief. It is commonly used in orthopedics, sports medicine, and urology.FSWT delivers high-intensity acoustic waves that penetrate deeply into tissues. These waves help:
- Stimulate blood flow and new blood vessel formation (angiogenesis)
- Promote cell regeneration and tissue repair
- Reduce inflammation and pain
- Break down calcifications in tendons
- Radial shockwave therapy Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses low- to medium-energy shockwaves to treat musculoskeletal conditions, especially those involving soft tissue injuries. Unlike Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT), which targets deep tissues with precise, focused waves, RSWT uses radial (spread-out) shockwaves that disperse over a broader area. RSWT works by delivering high-energy acoustic waves through a hand-held device. These waves spread outward in a radial pattern, targeting the surface layers of tissue. The shockwaves stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, promoting blood circulation and increasing metabolic activity in the treated area. Mechanism of Action
- Pain Relief: The shockwaves help reduce pain by stimulating the nerve fibers and triggering the body’s natural pain-reducing mechanisms.
- Improved Blood Circulation: The therapy promotes better blood flow, aiding in the healing of injured tissues.
- Collagen Production: RSWT encourages the production of collagen, which is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration.
Origins in medical use
Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT) has its origins in extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), a technique developed in the 1980s for breaking down kidney stones. The idea behind ESWL was to use high-energy sound waves to fragment kidney stones without the need for invasive surgery.
-
Transition to Musculoskeletal Use
In the early 1990s, researchers and physicians began exploring the potential of shockwave therapy for treating musculoskeletal conditions. They noticed that shockwaves had a therapeutic effect on soft tissues and tendons, promoting healing and reducing pain. This led to the development of focused shockwave therapy for conditions such as tendinopathies, calcific shoulder tendinitis, and plantar fasciitis.
-
Advancements and Applications
The technology behind shockwave therapy continued to evolve, with improvements in the precision and energy of the waves. Focused shockwave therapy (FSWT) was developed to target specific points deeper within the tissue, which made it more effective for treating conditions requiring focused, high-intensity energy.
Today, FSWT is widely used in orthopedics, sports medicine, and even in fields like urology (for conditions such as erectile dysfunction) and dermatology (for promoting tissue regeneration).
Would you like more details on the history or how the therapy is applied today?
How Does Shockwave Therapy Work?
Shockwave therapy works by delivering high-energy sound waves (acoustic waves) to specific areas of the body, which trigger biological responses that promote healing, reduce pain, and stimulate tissue regeneration. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how shockwave therapy works:
-
Generation of Shockwaves
The therapy begins with a specialised device that generates shockwaves—short, intense bursts of energy that travel through the skin and into the underlying tissues. These shockwaves are either focused (narrow and precise) or radial (broad and dispersed), depending on the type of shockwave therapy being used (Focused Shockwave Therapy or Radial Shockwave Therapy).
-
Shockwaves Penetrate the Tissue
The shockwaves penetrate the skin and underlying soft tissues (muscles, tendons, ligaments, etc.) at varying depths depending on the intensity and focus of the treatment. The shockwaves exert mechanical pressure on the tissue as they move through it.
-
Creation of Microtrauma and Biomechanical Stress
As the shockwaves travel through the tissue, they create tiny microtears or microtrauma in the treated area. This is a key part of the healing process, as the body perceives this as a form of injury, which then prompts it to initiate its natural healing mechanisms. The biomechanical stress from the shockwaves also stimulates the release of growth factors, which are essential for tissue regeneration.
-
Activation of Biological Healing Responses
- Pain Reduction Shockwaves stimulate nerve fibers, which can block pain signals, providing immediate pain relief. The therapy also promotes the release of endorphins (natural painkillers), further reducing pain.
- Increased Blood Flow and Circulation The shockwaves improve vascularization in the treated area, leading to the formation of new blood vessels. This increased blood flow enhances the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the injured tissues, which accelerates the healing process.
- Collagen Production The therapy activates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen, a protein vital for tissue repair. Increased collagen production leads to stronger and more resilient tissues in the healing area.
- Tissue Regeneration Shockwaves stimulate the activity of mesenchymal stem cells in the damaged tissue, promoting regeneration and repair. These cells can differentiate into various types of tissue cells, assisting in the healing of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and even bone.
- Breakdown of Calcifications In conditions like calcific tendinitis, where calcium deposits build up in the tendons, shockwave therapy helps to break down these deposits. The shockwaves fragment the calcifications, making it easier for the body to absorb them, reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Reduced Inflammation: Shockwaves can reduce inflammation by promoting the release of cytokines, which help regulate the immune system and control inflammation in the affected area.
- Restoring Function and Reducing Scar Tissue As the body heals, scar tissue is reduced, and tissues regain their normal structure and function. Over time, repeated sessions of shockwave therapy can help prevent the formation of dense scar tissue and improve mobility, flexibility, and strength in the treated area.
- Long-Term Benefits Chronic injuries and pain can be alleviated through multiple treatments. Shockwave therapy can reduce pain, enhance recovery time, and prevent the recurrence of injuries by promoting long-term healing and tissue regeneration.

Medical and Therapeutic Applications
Due to its ability to stimulate healing and reduce pain, shockwave therapy is widely used across various medical fields:
Orthopaedic Use
Shockwave therapy has become a highly effective treatment for a wide range of orthopedic conditions, particularly those related to musculoskeletal injuries and chronic pain. In orthopedics, shockwave therapy is used to treat both acute and chronic conditions that involve soft tissue, bones, tendons, and joints. Here’s an overview of how shockwave therapy is used in orthopedics:
1. Tendon Injuries
Tendons are frequently subject to injuries, particularly in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive motions. Shockwave therapy is effective in treating tendinopathies (tendon injuries or inflammation) by stimulating healing and improving tissue function.
Common Tendon Injuries Treated:
- Achilles tendinopathy (pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon)
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) (pain on the outside of the elbow)
- Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) (pain on the inside of the elbow)
- Rotator cuff tendinopathy (shoulder tendon injuries)
- Patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee)
- Plantar fasciitis (heel pain, particularly inflammation of the plantar fascia tendon)
2. Sports Medicine
Athletes often experience musculoskeletal injuries due to high-impact movements, repetitive strain, and overuse. Shockwave therapy is widely used in sports medicine to accelerate recovery, reduce pain, and enhance mobility by promoting tissue repair and improving circulation.
Common Sports Injuries Treated:
- Muscle Strains – Helps heal microtears in muscle fibres, reducing pain and improving flexibility.
- Shin Splints (Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome) – Reduces inflammation and promotes healing in the lower leg.
- Stress Fractures – Supports bone healing by stimulating blood flow and cellular regeneration.
- IT Band Syndrome (Iliotibial Band Syndrome) – Relieves tension and inflammation along the outer thigh.
- Hamstring Injuries – Speeds up recovery by enhancing muscle repair and reducing scar tissue formation.
- Hip Pain & Bursitis – Alleviates discomfort caused by overuse and inflammation in the hip joint.
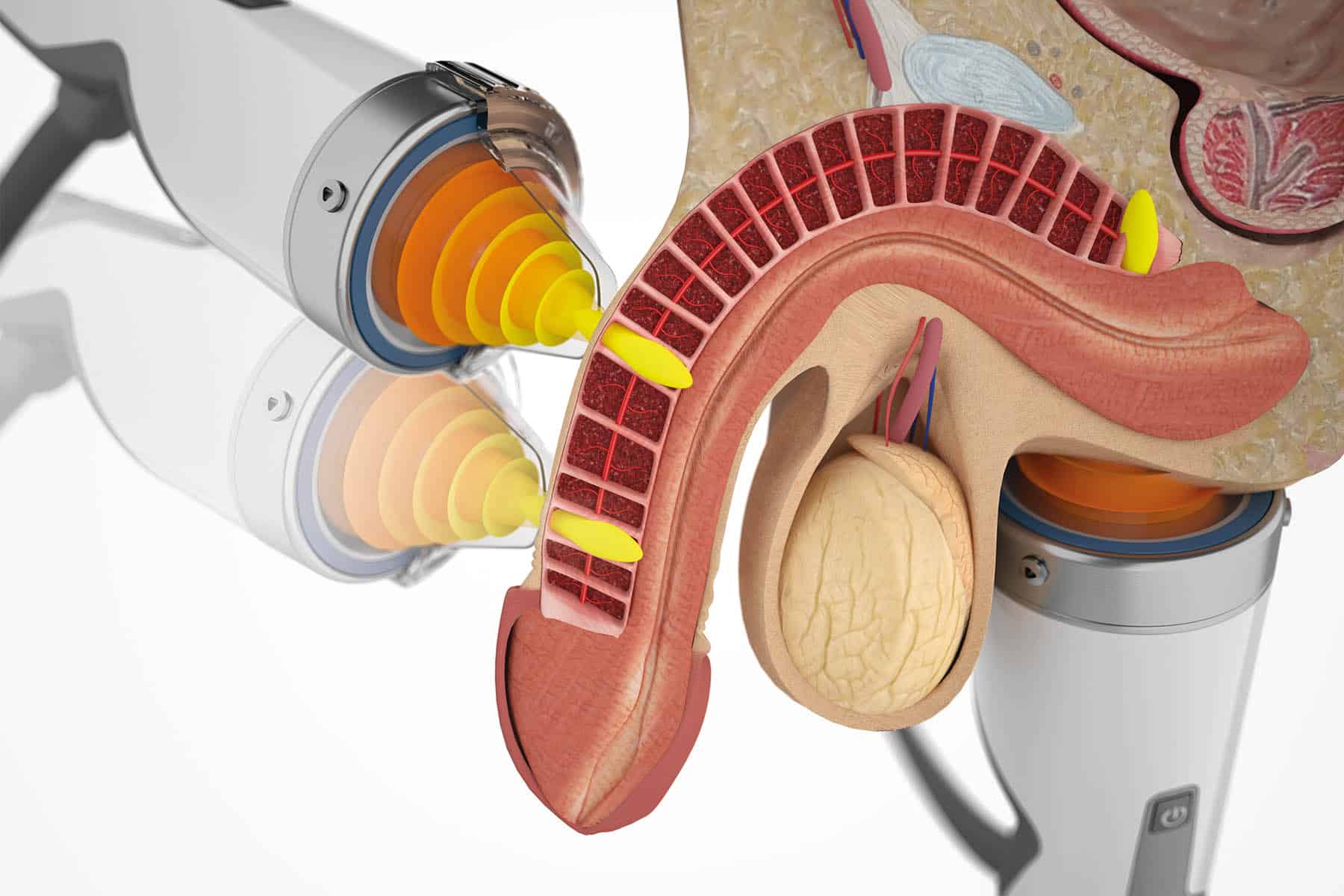
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Treatment
One of the most significant advancements in shockwave therapy is its use in erectile dysfunction treatment. By improving blood flow to the penile tissue, it often helps men achieve and maintain stronger erections. Studies have shown that shockwave therapy can be particularly effective for individuals with vascular-related ED, offering a non-invasive alternative to surgery and medication.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Treating ED:
- Improved Blood Flow – Stimulates the formation of new blood vessels and enhances circulation to the penile tissue, helping men achieve and maintain stronger erections.
- Non-Invasive Treatment – Provides a surgery-free alternative to traditional erectile dysfunction treatments with minimal discomfort and downtime.
- Long-Term Results – Encourages natural tissue to regenerate and repair, leading to sustained improvements in erectile function over time.
- No Medication Required – Reduces the need for oral medications, such as PDE5 inhibitors, making it a suitable option for men who cannot take or do not respond well to ED drugs.
Aesthetic & Dermatological Uses
Used for promoting skin regeneration and improving tissue health, shockwave therapy is increasingly utilised for aesthetic and dermatological treatments. By stimulating collagen production and enhancing blood circulation, it can help reduce signs of ageing, improve skin texture, and support the healing of various skin conditions.
Common Aesthetic & Dermatological Uses:
- Cellulite Reduction – Breaks down fat deposits and stimulates collagen production, leading to smoother, healthier skin.
- Scar and Stretch Mark Treatment – Boosts tissue repair and regeneration to reduce the appearance of scars and stretch marks.
- Skin Tightening and Rejuvenation – Enhances collagen production to improve skin elasticity and overall appearance.
- Wound Healing and Ulcer Treatment – Accelerates healing by improving blood flow and reducing inflammation in chronic wounds and ulcers.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Shockwave therapy provides numerous benefits, making it an attractive option for many conditions:
- Non-invasive treatment – no need for surgery or medication.
- Minimal downtime compared to surgical procedures.
- Effective for various conditions, including erectile dysfunction, tendon injuries and chronic pain.
- Clinically proven to stimulate tissue regeneration and improve healing outcomes.
- Low risk of complications when administered by a qualified specialist.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While shockwave therapy is generally safe, some mild side effects include:
- Temporary pain or discomfort during or after treatment.
- Redness, swelling, or bruising in the treated area.
- Numbness or tingling, which usually eases within a few days.
Certain individuals may not be suitable for shockwave therapy. Those with blood clotting disorders, active infections or pacemakers, as well as pregnant women, should consult a healthcare provider before considering shockwave treatment.
What to Expect During a Shockwave Therapy Session
A shockwave therapy session involves:
Initial Consultation – A specialist first assesses the patient’s condition and medical history to determine if shockwave therapy is appropriate.
Treatment Procedure – A gel is applied to the targeted area and a handheld device is used to deliver acoustic waves. The procedure is generally well-tolerated, with mild discomfort for some individuals.
Post-Treatment Care – Most patients resume daily activities immediately after treatment, with noticeable improvement often seen after a few sessions.
Number of Sessions – The number of sessions required depends on the condition being treated, but most individuals undergo three to six sessions for optimal results.
Is Shockwave Therapy Right for You?
Shockwave therapy offers a non-invasive, clinically proven treatment for those struggling with chronic pain, sports injuries and erectile dysfunction. While it is effective for many, it is not suitable for everyone, making an initial consultation with an experienced professional essential.


