Ear wax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal to protect and clean the ears. When it builds up in excess, it can cause discomfort, hearing loss or even infection; making it crucial to understand when removal is necessary and to choose the safest and most effective treatment method.
When Is Ear Wax a Problem?
Common Symptoms – Blocked Ears, Hearing Loss, Discomfort
Ear wax build-up can lead to noticeable changes in hearing, a sensation of fullness or blockage in the ear, as well as general discomfort. In some cases, people may also experience ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or dizziness.
When and Why to Avoid DIY Removal
Using cotton buds or hairpins to try and clear ear wax at home can harden wax and push it further into the canal, making the problem worse. There’s also a risk of damaging the delicate ear canal or eardrum, especially if there’s a pre-existing condition.
Risks of Ignoring Excess Wax
Leaving a significant build-up untreated can increase the risk of ear infections, temporary hearing loss and persistent discomfort. For some, wax impaction can affect balance or cause coughing due to pressure on the vagus nerve.
Professional Ear Wax Removal Methods
Clinically approved ear wax removal techniques recommended by audiologists and GPs are very often safer and more effective than home remedies.
Microsuction
Microsuction is a quick, precise and minimally invasive procedure that uses gentle suction to remove earwax. It is considered one of the safest and most effective methods, particularly for complex or hard blockages.
Irrigation (Ear Syringing)
Irrigation, or ear syringing as it is also known, involves flushing the ear canal with warm water to dislodge and clear wax. It is effective for many patients but isn’t suitable for those with ear infections, perforated eardrums or previous ear surgery.
Manual Removal (Curettage)
In cases where wax is clearly visible and near the outer ear canal, a clinician may use specialised tools to manually extract it. This method is often used in conjunction with suction or irrigation.
Over-the-Counter and Home Remedies
Below we explore the effectiveness and safety of non-clinical options:
Softening Drops (Olive Oil, Hydrogen Peroxide)
Softening drops, often containing olive oil, can help soften impacted wax. This softening can make it easier to expel wax naturally or remove during professional treatment. They’re often recommended as a first step but should be used with care if you’ve had ear problems before.
Ear Candling – Why It’s Not Recommended
Despite being marketed as a natural remedy, ear candling is ineffective and potentially dangerous. It can cause burns, wax residue and even perforate the eardrum. Medical professionals strongly advise against its use.
Steam and Warm Compresses
Applying gentle steam or a warm flannel may relieve symptoms of blockage temporarily by loosening wax. However, this method alone is unlikely to remove significant build-up and should be used with caution.
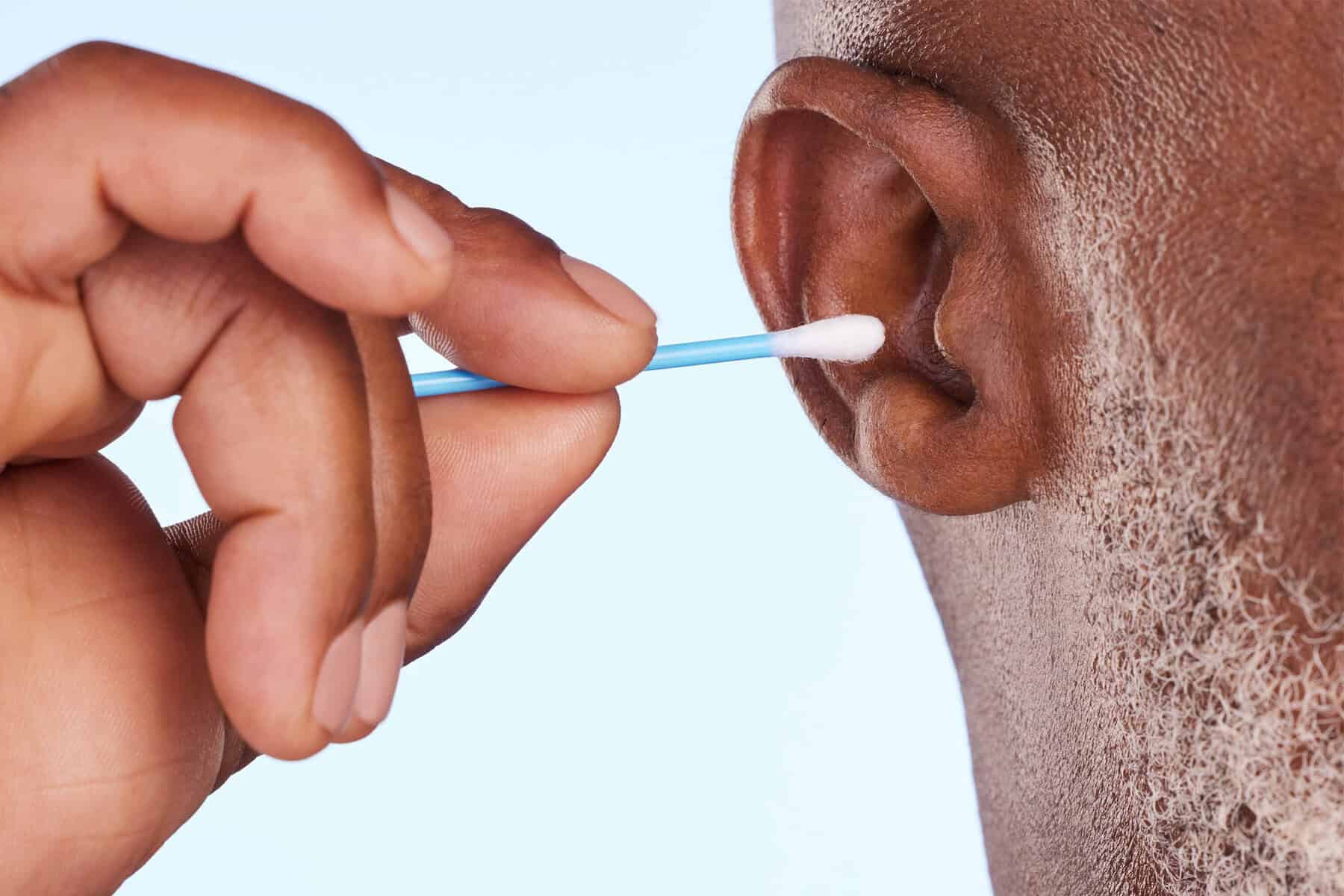
Risks of Using Cotton Buds or Objects
Inserting objects into your ear can push wax deeper or injure the ear canal and eardrum. It’s a common cause of worsening blockages and should always be avoided.
Choosing the Best Method for You
The most suitable treatment method depends on the type of patient and severity of earwax build-up.
Mild Blockage vs. Severe Build-Up
If symptoms are mild, drops or steam may offer relief. Severe build-up typically needs professional intervention such as microsuction or irrigation.
Underlying Conditions (e.g. Ear Infections, Perforated Eardrums)
Individuals with recurring infections, past surgery or eardrum perforations should avoid irrigation and seek specialist advice to determine the safest removal method.
Children, Older Adults and Frequent Wax Buildup
Paediatric or geriatric patients may require gentler methods due to narrower or more sensitive ear canals. Those with frequent blockages can benefit from regular check-ups and a personalised care plan.
When to See an Ear Specialist
If you’ve tried over-the-counter methods and have not experienced relief or you have ongoing symptoms, it’s important to consult a professional.
Safe diagnosis and long-term management can prevent complications. An ENT specialist can identify whether your symptoms are related to wax or another issue, such as an ear infection.
During a clinical appointment, you can expect a thorough examination of your ear canal using a microscope or video otoscope, followed by safe and effective treatment.
Prioritise Ear Health and Safety
While some home remedies can help with mild symptoms, ear wax removal is often best left to trained professionals. Your ears are sensitive and essential to everyday life, so protecting them with safe, targeted treatment is crucial.
Book an appointment at The Forbury Clinic for precision ear wax removal and benefit from clearer, healthier hearing.


