Kidney stones are a common and painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These hard mineral deposits form in the kidneys and can cause significant discomfort as they pass through the urinary tract. While kidney stones are prevalent, they can often be prevented with the right lifestyle and dietary changes.
Preventing kidney stones is crucial because they not only cause intense pain but can also lead to complications such as infections or the need for surgery. By understanding the factors that contribute to kidney stone formation, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk.
In this article, we will explore what kidney stones are, the various types, and the common risk factors. Additionally, we’ll provide practical tips and strategies to help you stay stone-free, ensuring better urinary health and a lower chance of recurrence.
Understanding Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are solid masses made up of crystals that separate from your urine within the kidneys. They can vary in size, ranging from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Kidney stones form when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, which can clump together to create a stone.
There are several types of kidney stones, each with a different cause:
- Calcium Oxalate Stones: The most common type, formed when calcium combines with oxalate in the urine.
- Uric Acid Stones: These develop when the urine is too acidic, often due to a diet high in purines, found in red meat and shellfish.
- Struvite Stones: Typically associated with infections, these stones can grow quickly and become quite large.
- Cystine Stones: A rare type caused by a genetic disorder that leads to the excretion of too much cystine, an amino acid, in the urine.
Statistics show that kidney stones are quite common, with a lifetime risk of 10-15% in the general population. Unfortunately, once you’ve had a kidney stone, your risk of recurrence increases, with nearly 50% of individuals experiencing another stone within five years.
Common Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing kidney stones:
- Gender and Age: Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women, and the risk increases with age, particularly in those aged 30-60.
- Family History: A family history of kidney stones significantly raises your chances of developing them, as genetic factors can influence stone formation.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Choices: Diets high in sodium, protein, and oxalate-rich foods (like spinach and nuts) can elevate the risk of kidney stones. Additionally, inadequate hydration and a sedentary lifestyle are significant contributors.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as gout, hyperparathyroidism, and urinary tract infections, can predispose individuals to kidney stone formation.
Understanding these risk factors is the first step in taking control of your kidney health and adopting preventive measures to stay stone-free.
Dietary Changes to Prevent Kidney Stones
Making specific dietary changes is essential in reducing the risk of kidney stones. By adjusting your fluid intake and being mindful of the foods you consume, you can significantly decrease your chances of developing stones.
Hydration is Key
One of the most effective ways to prevent kidney stones is to stay well-hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps dilute the substances in your urine that can form stones, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid. Aim to drink at least 2-3 litres of water per day, or enough to produce clear or light-yellow urine. In hot weather or when engaging in physical activity, you may need even more fluids to stay hydrated and maintain a healthy urinary system.
Limit Sodium Intake
High sodium intake is a known contributor to kidney stone formation. Excess salt in your diet increases the amount of calcium in your urine, which can lead to the development of calcium oxalate stones. To reduce your sodium intake, limit processed and packaged foods, which often contain high levels of salt. Cooking at home with fresh ingredients allows you to control the amount of salt in your meals. Additionally, try using herbs and spices to flavour your food instead of relying on salt.
Watch Oxalate-Rich Foods
Oxalates are naturally occurring substances found in many foods, and consuming them in large quantities can increase your risk of kidney stones. Foods high in oxalates include spinach, nuts, tea, chocolate, and beets. While it’s not necessary to eliminate these foods entirely, it’s essential to consume them in moderation, especially if you are prone to kidney stones. Pairing oxalate-rich foods with calcium-rich ones during meals can also help prevent stone formation, as calcium binds to oxalate in the stomach and intestines, reducing the amount that reaches the kidneys.
Balance Calcium Intake
Calcium plays a crucial role in preventing kidney stones, contrary to the common misconception that calcium-rich foods should be avoided. Adequate calcium intake helps reduce the absorption of oxalate in the body, which can lead to stone formation. Adults should aim for 1,000-1,200 milligrams of calcium per day. Excellent dietary sources of calcium include dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yoghurt, as well as leafy green vegetables and fortified plant-based alternatives. It’s important to get calcium from food rather than supplements, as excessive calcium supplementation can increase the risk of stones.
By making these dietary adjustments, you can take proactive steps to prevent kidney stones and support your overall kidney health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adjusting your lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of developing kidney stones. Simple changes in daily habits can have a lasting impact on your kidney health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
There is a strong link between obesity and the risk of kidney stones. Excess body weight can lead to changes in the urine composition, increasing the likelihood of stone formation. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular physical activity and a balanced diet is essential for reducing this risk. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week, and focus on consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Consistency in these habits can help manage your weight effectively and support overall kidney health.
Monitor Vitamin and Supplement Intake
While vitamins are crucial for overall health, excessive intake of certain vitamins, particularly vitamin C and D, can increase the risk of kidney stones. High doses of vitamin C can raise oxalate levels in the urine, while too much vitamin D can lead to increased calcium in the urine, both contributing to stone formation. To prevent this, follow the recommended daily allowances for these vitamins and consult with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements. It’s important to balance your nutrient intake to avoid inadvertently increasing your risk of kidney stones.
Medical Interventions
For individuals at higher risk of kidney stones, medical interventions may be necessary to prevent recurrence and manage the condition effectively.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Routine medical check-ups are vital for those who have had kidney stones or are at risk. Regular urine and blood tests can help monitor your body’s tendency to form stones by assessing levels of minerals and other substances in your body. Early detection of any abnormalities allows for timely intervention, potentially preventing stone formation before it becomes a problem. These check-ups provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider and make adjustments to your prevention plan as needed.
Medications and Treatments
In addition to lifestyle changes, certain medications and treatments can help prevent the formation of kidney stones. Urologists may prescribe medications that reduce stone formation by altering the composition of urine, such as thiazide diuretics for calcium stones or allopurinol for uric acid stones. In some cases, more advanced treatments like shock wave lithotripsy may be recommended to break down stones that have already formed. Your urologist will tailor treatment options to your specific needs, ensuring the best approach to prevent future kidney stones.
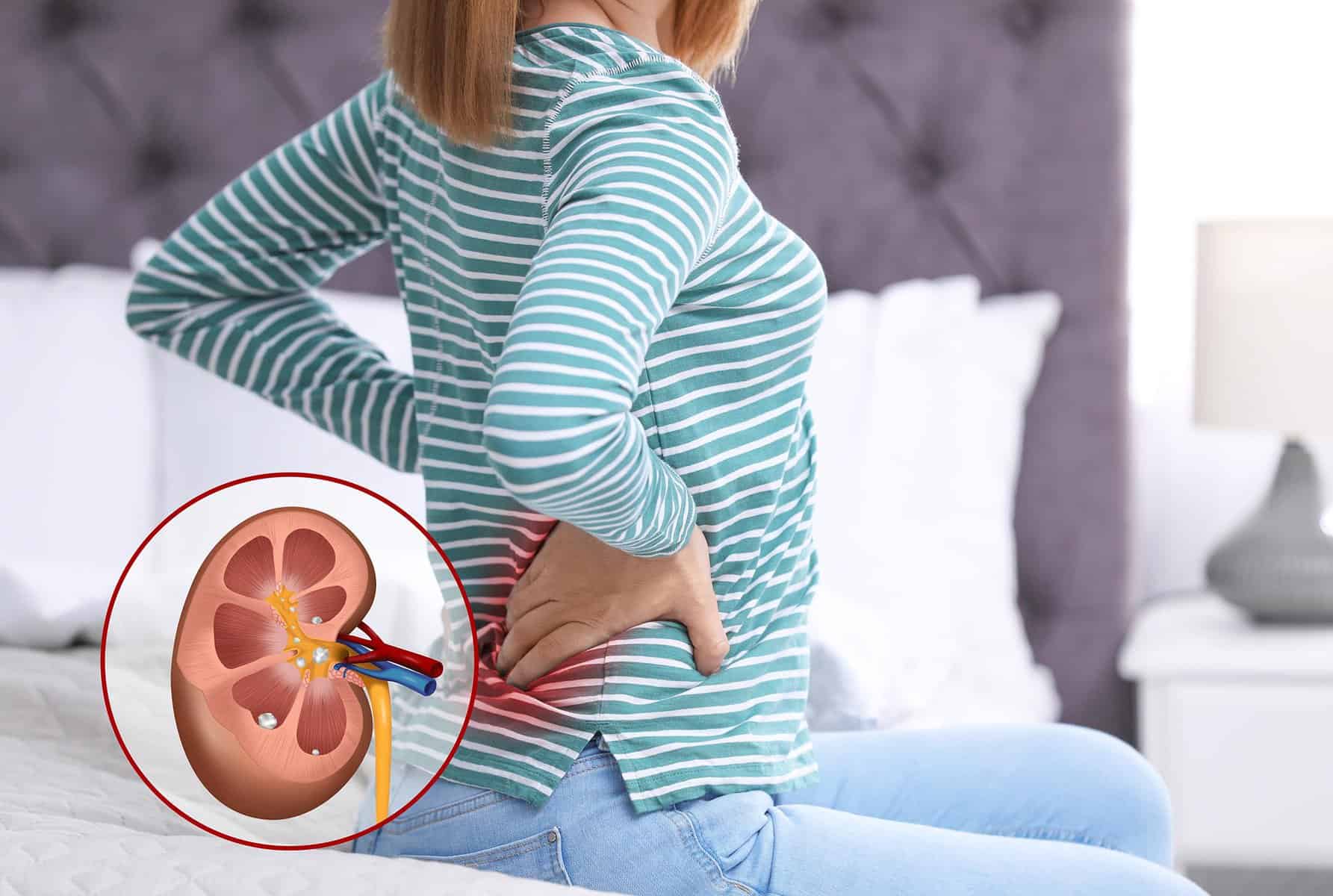
Recognising Symptoms Early
Understanding the early signs of kidney stones can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of complications.
Common Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones often present with symptoms like severe pain in the lower back or side, blood in the urine, nausea, and frequent or painful urination. Recognising these symptoms early is crucial for prompt medical attention, which can significantly reduce the severity of the condition.
Importance of Early Detection
Seeking medical attention at the first sign of symptoms can simplify treatment and improve recovery outcomes. Early detection allows for less invasive treatments and prevents stones from growing larger or causing more severe health issues. If you experience any symptoms associated with kidney stones, contact your healthcare provider immediately to discuss the best course of action.
Myths and Facts about Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are surrounded by many myths that can lead to confusion. One common myth is that consuming dairy products always causes kidney stones. In reality, moderate calcium intake from dairy can help prevent stones by binding with oxalate in the digestive tract. Another misconception is that only men get kidney stones, but women are also at risk. Understanding the facts about kidney stones is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Educating yourself with accurate information can help you make better choices to protect your kidney health.
Preventing Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are a common yet preventable condition. By understanding the risk factors, making dietary and lifestyle changes, and seeking regular medical care, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing kidney stones. Early recognition of symptoms and debunking common myths are also crucial steps in maintaining kidney health. Implement the tips shared in this article to stay stone-free and ensure long-term well-being. Taking proactive measures today can save you from the discomfort and complications of kidney stones in the future.
Share this article with your family and friends to spread awareness about kidney stone prevention. If you have any concerns or need personalised advice, consult your healthcare provider. For more information or to schedule a consultation, contact us. Taking steps now can help you and your loved ones stay healthy and stone-free.

