Prostate cancer is a major health concern for men, particularly in the UK, where it stands as one of the most common types of cancer. The prostate gland, part of the male reproductive system, is where this cancer originates. Often, prostate cancer progresses slowly and may not show symptoms until it’s more advanced, making early detection crucial. Regular screening is key to identifying prostate cancer in its early stages, where treatment is most effective and survival rates are significantly higher.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Understanding prostate cancer is essential to recognising its impact and the importance of early detection.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow uncontrollably, forming a tumour. The prostate is a small gland responsible for producing seminal fluid, essential for nourishing and transporting sperm. While many cases of prostate cancer are slow-growing and confined to the gland, some can be aggressive and spread rapidly. Understanding the nature of prostate cancer is vital, as early detection through screening can lead to more successful treatment outcomes.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. Age is the most significant, with men over 50 being at the highest risk. A family history of prostate cancer also elevates risk, particularly if close relatives like a father or brother have been diagnosed. Lifestyle factors, including diets high in red meat and dairy or low in fruits and vegetables, may contribute to an increased risk. Ethnicity is another important factor, with Black men being more likely to develop prostate cancer than men of other ethnicities. Understanding these risk factors highlights the importance of regular screening and early detection.

The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of prostate cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival. Understanding the value of screening can help men make informed decisions about their health.
Why Early Detection Matters
Detecting prostate cancer in its early stages is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, early-stage prostate cancer often has a higher survival rate, as the cancer is usually confined to the prostate gland and has not spread to other parts of the body. This localisation allows for more treatment options, including less invasive procedures, which can lead to better outcomes and a quicker recovery. Additionally, when detected early, prostate cancer can be monitored more effectively, and interventions can be planned strategically, reducing the need for aggressive treatments and preserving the patient’s quality of life.
Consequences of Late Detection
Late-stage detection of prostate cancer can lead to a range of complications and increased risks. As the cancer progresses, it may spread to other organs, such as the bones and lymph nodes, making treatment more complex and less effective. Patients diagnosed at a later stage often face limited treatment options, which can be more invasive and carry a higher risk of side effects. Furthermore, the chances of survival decrease significantly with late-stage prostate cancer, underscoring the critical need for regular screening and early intervention.
Types of Prostate Cancer Screening Tests
Several screening methods are available to detect prostate cancer early, each with its own benefits and limitations.
PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Test
The PSA test measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. PSA is a protein produced by both cancerous and non-cancerous tissues in the prostate. Elevated levels of PSA in the blood may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, prompting further investigation. The PSA test is a widely used tool in the early detection of prostate cancer, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
The Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) is another common screening method for prostate cancer. During a DRE, a healthcare provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland for any irregularities or lumps. While the DRE can help detect abnormalities in the prostate, it is often used in conjunction with the PSA test for a more comprehensive assessment.
Other Diagnostic Tests
In addition to the PSA test and DRE, other diagnostic tools may be employed to further evaluate prostate health. These can include MRI scans, ultrasounds, and biopsies, which provide more detailed information about the prostate and help confirm the presence of cancer. These additional tests are particularly useful when initial screening results are inconclusive or when more information is needed to guide treatment decisions.
Who Should Get Screened?
Screening recommendations for prostate cancer vary based on age, risk factors, and individual health considerations.
Age and Screening Guidelines
Men are generally advised to start prostate cancer screening around the age of 50. However, those with higher risk factors may need to begin earlier. Regular screening, typically every two years, is recommended for men between the ages of 50 and 70. After 70, screening decisions should be based on individual health status and preferences.
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups are at higher risk for prostate cancer and may need to consider earlier and more frequent screenings. This includes men with a family history of prostate cancer, those of African or Caribbean descent, and individuals with certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2. These high-risk groups should discuss personalised screening schedules with their healthcare providers to ensure early detection and timely intervention.
What to Expect During Screening
Prostate cancer screening is a straightforward process, and understanding what to expect can help ease any concerns.
Preparation for Screening
Before your screening, it’s important to discuss any medications you’re taking with your healthcare provider, as some can affect PSA levels. Also, try to avoid activities that might irritate the prostate, like cycling, just before the test.
The Screening Process
During the PSA test, a simple blood sample is taken to measure your PSA levels. The Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) involves a brief physical examination of the prostate, which can feel slightly uncomfortable but is quick. Both tests are usually completed in a short visit, making them convenient and accessible.
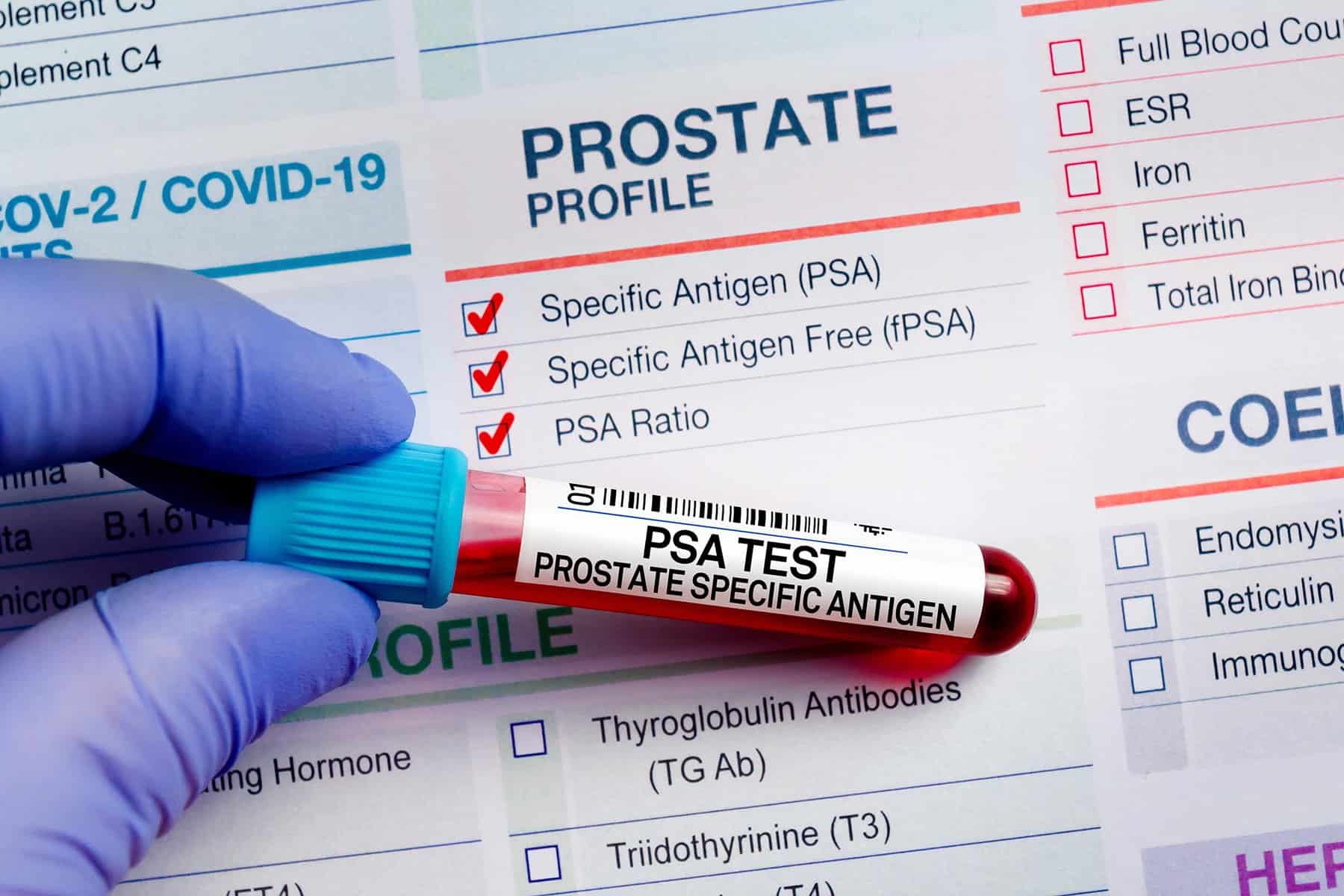
Interpreting Screening Results
Understanding the results of your prostate cancer screening is crucial for determining the next steps in your healthcare.
Understanding PSA Levels
PSA levels are measured in nanograms per millilitre (ng/mL). A higher PSA level can indicate prostate cancer, but it may also be caused by other conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or inflammation. Your doctor will interpret your PSA level in the context of your overall health and age.
Next Steps After Abnormal Results
If your PSA level is elevated or your DRE results are abnormal, your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as an MRI or a biopsy, to get a clearer picture. These follow-up tests help to confirm whether cancer is present and determine the best course of action.
Common Myths About Prostate Cancer Screening
There are several misconceptions about prostate cancer screening that can prevent men from seeking the care they need.
Debunking Screening Myths
One common myth is that prostate cancer screening is only necessary if symptoms are present. In reality, early-stage prostate cancer often has no symptoms, making screening essential for early detection. Another myth is that screening is always painful or invasive, but most tests, like the PSA and DRE, are quick and minimally uncomfortable. Finally, some believe that a high PSA level always means cancer, which isn’t true. Elevated PSA can be caused by other conditions, and further tests are needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Regular screening for prostate cancer is a critical step in maintaining men’s health.
Early detection through regular screening can significantly improve treatment outcomes and save lives. It’s an essential part of managing your health.
Don’t wait – talk to your healthcare provider about prostate cancer screening today. Schedule your appointment and encourage others to get screened to ensure their health and well-being.


